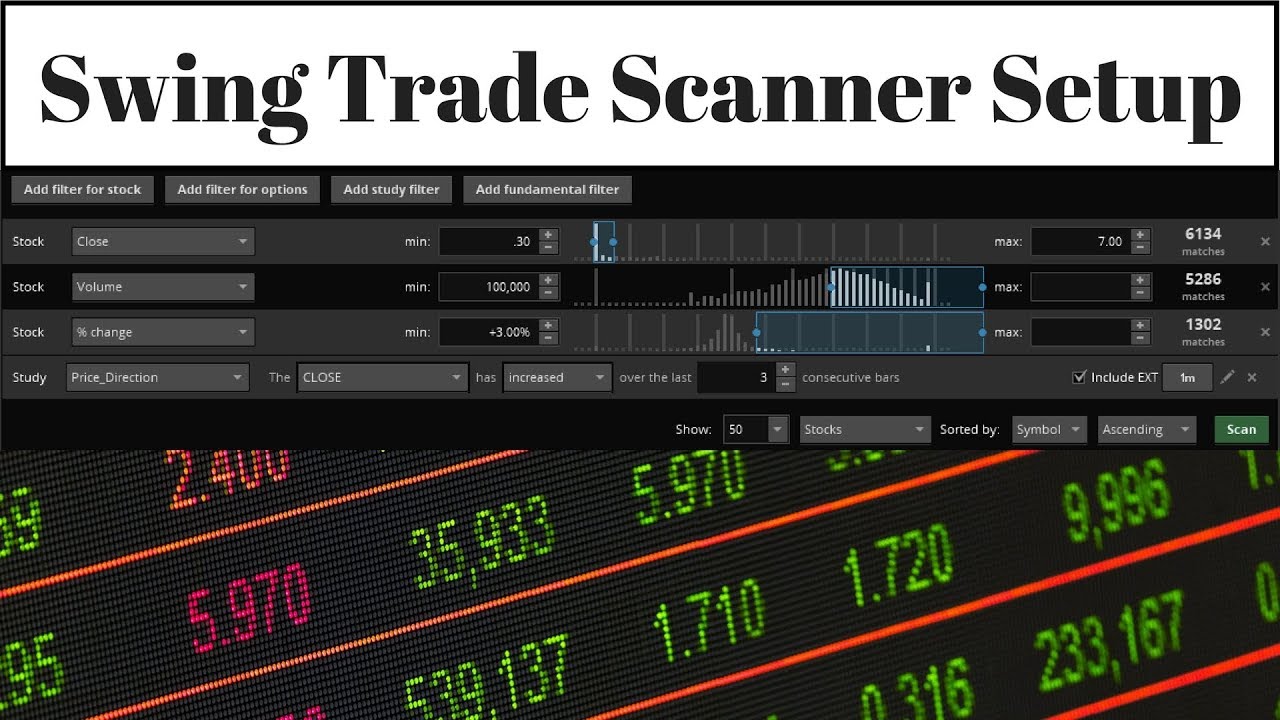
How can automated tools identify profitable short-term trading opportunities? A critical tool in the modern trader's arsenal is a software that automatically searches for potential swing trade opportunities.
A software application designed for scanning financial markets to detect patterns and signals indicative of potential swing trade setups is known as a swing trade scanner. These tools typically analyze historical price data, volume, and other relevant factors, flagging stocks, forex pairs, or other instruments that meet predefined criteria. For instance, a scanner might flag a stock whose price has broken a key support or resistance level along with a volume spike, suggesting a possible reversal pattern. The scanner then generates alerts, informing the user of the detected potential opportunities.
These tools are valuable for several reasons. They can process vast amounts of data much faster than humans, allowing traders to identify potential trades more efficiently. Furthermore, the objectivity of the scanner can reduce emotional bias, ensuring that trading decisions are grounded in quantitative analysis rather than gut feeling. The speed and thoroughness of a well-implemented scanner can also free up the trader's time, allowing them to focus on other aspects of their strategy. However, the scanner is only a tool. Fundamental analysis or further technical study should be performed to confirm the scanner's alerts before any actual trade. No tool guarantees success in the markets. Importantly, they enhance the trader's ability to systematically scan the market for opportunities, thereby optimizing potential gains.
Read also:Your Comprehensive Guide How To Turn Smok Vape On
These tools assist traders in efficiently identifying swing trading opportunities, but they are not a guaranteed formula for success. The decision to buy or sell a security remains a personal one, and careful consideration of all factors is paramount.
Swing Trade Scanner
Swing trade scanners are software tools designed to expedite the identification of potential profitable short-term trading opportunities. Their efficacy hinges on the accuracy and thoroughness of their analysis of market data.
- Data Analysis
- Pattern Recognition
- Alert Generation
- Market Timing
- Risk Management
- Backtesting Capabilities
A swing trade scanner's effectiveness depends on its ability to process large datasets quickly and accurately (Data Analysis). It identifies recurring patterns and signals (Pattern Recognition), creating alerts for potential swing trades. Effective market timing (Market Timing) necessitates identifying the right entry and exit points. Robust scanners often include risk management tools (Risk Management) to assess potential losses. Backtesting capabilities (Backtesting Capabilities) validate the scanner's performance. Real-world examples include software using technical indicators like moving averages or volume to identify trends and potential reversal points for swing trades. Ultimately, a well-designed scanner streamlines the process of identifying potential trade setups and enhances informed trading decisions. However, no trading system is foolproof. Manual confirmation of scanner alerts and proper risk management are crucial for successful trading.
1. Data Analysis
Data analysis forms the bedrock of any effective swing trade scanner. The accuracy and efficacy of a scanner are directly linked to the comprehensiveness and reliability of the data it processes. Successful identification of potential swing trading opportunities hinges on the ability to extract meaningful information from market data.
- Historical Price Data Analysis
Scanners often leverage historical price charts to identify patterns and trends. This includes analyzing open, high, low, and close (OHLC) data, identifying support and resistance levels, and recognizing various candlestick patterns. The precision and timeliness of this historical data significantly impact the scanner's ability to flag potential entry and exit points for swing trades. Sophisticated algorithms analyze volume alongside price movements to strengthen the reliability of identified patterns. This data analysis is crucial for identifying historical trading patterns that could potentially repeat.
- Volume Analysis
Volume data, representing the quantity of shares traded, provides additional context to price movements. A surge in volume accompanying a price increase can be a strong signal of a potential upward trend, while a significant decrease in volume alongside price stagnation might suggest a weakening trend. Incorporating volume data into the analysis adds another layer of insight for scanners, potentially increasing the accuracy of trade signal detection. The scanner utilizes this volume data to determine the strength of the price movement.
Read also:
- Free Ullu Watch Movies Shows Online
- Technical Indicator Analysis
Many scanners use a wide array of technical indicators, such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and MACD, to filter market data. These indicators, calculated from historical price and volume data, can provide insights into market momentum, overbought/oversold conditions, and potential trend reversals. The accurate calculation and interpretation of these indicators are crucial for the reliability of the signals provided by the scanner, allowing it to highlight potentially profitable swing trade setups based on identified market dynamics. This facet highlights how mathematical models are used to automate trade analysis.
- Market Sentiment Analysis (Optional)
Some advanced scanners incorporate market sentiment analysis, gleaning data from social media, news articles, and other publicly available sources. This can provide a qualitative understanding of market sentiment toward a given security, potentially informing the scanner's decision-making process. Adding this layer of analysis allows for a more holistic view of the market environment, but the reliability and integration of such data into the scanning process can pose challenges.
Effective data analysis in a swing trade scanner is paramount. Accurate analysis of historical price data, volume, technical indicators, and potentially market sentiment creates a system that identifies potentially successful swing trading opportunities. However, it's vital to remember that no trading system is guaranteed to succeed. It is crucial for the user to apply prudent judgment, performing additional due diligence and analysis on the flagged signals before acting on any trade recommendations.
2. Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition is a critical component of a swing trade scanner. The efficacy of such software relies heavily on its ability to identify recurring patterns in market data. These patterns, often subtle, can suggest potential future price movements. Understanding how a scanner identifies these patterns is vital for evaluating its reliability and potential success. This exploration highlights the methods through which a scanner seeks to spot repeatable market behaviors.
- Trend Identification
A fundamental aspect of pattern recognition in a swing trade scanner is identifying trends. Software might recognize ascending or descending price patterns over a given timeframe, perhaps a few weeks or months. A consistent upward trajectory, for instance, could suggest a long-term bullish trend, while a downward trend could point toward a bearish outlook. The scanner uses algorithms to analyze the continuity of these price movements and flag potential opportunities based on this trend determination. The accuracy of the identified trend is crucial for the scanner's predictive value.
- Support and Resistance Levels
Scanners often use pattern recognition to identify support and resistance levels. Support is a price level where the market has historically shown strength in resisting downward pressure; resistance is a price level where the market frequently stalls after upward movement. By recognizing these patterns, the scanner can identify potential areas of buying or selling pressure. A break of these levels, often associated with increased volume, can indicate a potential change in trend, offering possible entry or exit points for swing trades. The reliability of a scanner is contingent on the correct identification of these pivotal price levels.
- Candlestick Patterns
Recognizing candlestick patterns is another critical aspect of pattern recognition. Specific configurations of candlestick shapes can indicate potential reversals or continuations of price movements. For example, a bearish engulfing pattern may suggest a trend reversal. The scanner would analyze these patterns across multiple timeframes to filter out noise and isolate potentially accurate predictive indicators. The scanner's ability to correctly interpret these patterns is crucial for its overall performance.
- Volume Patterns and Correlations
Pattern recognition goes beyond price alone. A scanner should also recognize volume patterns, such as sudden increases or decreases in trading volume, which may accompany price changes. Volume patterns often highlight the strength of a price movement, potentially indicating increased investor interest or a change in market sentiment. A scanner's ability to correlate volume with price actions is vital in discerning the significance of a particular market event or pattern. Correctly detecting these correlated changes aids in accurate trade signal identification.
In summary, a swing trade scanner relies on pattern recognition to identify potentially profitable swing trading opportunities. The accuracy and effectiveness of this pattern recognition directly influence the scanner's overall performance. The ability of the scanner to discern trends, support and resistance, candlestick patterns, and volume correlations is pivotal for its success. However, reliance on pattern recognition alone is not a guarantee of profit; traders must apply their own judgment and conduct further analysis before making trading decisions.
3. Alert Generation
Alert generation is a crucial function within a swing trade scanner. It serves as the conduit for translating the scanner's analysis into actionable information for the trader. The scanner's core purpose identifying potential swing trade opportunities is effectively realized through the timely and accurate generation of alerts. Without robust alert generation, the entire process of using a swing trade scanner is severely hampered. Alerts inform traders of potential market movements, guiding potential entry and exit points.
The significance of alert generation stems from its ability to automate a significant portion of the trading process. By swiftly identifying patterns meeting predetermined criteria, the scanner minimizes the time required for human analysis. This automated process facilitates faster reaction times, potentially crucial in capturing profitable swing trades, and allows traders to monitor multiple markets simultaneously. A well-designed alert system ensures that potentially lucrative opportunities are not missed due to human oversight or delayed observation. Examples include alerts generated when a stock's price breaks a key support level, suggesting a potential downtrend, or a volume surge with a price increase, signaling a strong upward trend. These alerts provide critical information to inform a trader's decision-making process.
Accurate and timely alert generation is paramount to leveraging the benefits of a swing trade scanner. However, the system's alerts should not be interpreted as infallible signals. Proper risk management, fundamental analysis, and supplementary technical analysis are essential before acting on any alert. Furthermore, the frequency of alerts and the criteria employed for their generation are crucial settings that traders must carefully configure to avoid an overwhelming number of false signals. An excessive amount of alerts can lead to trader fatigue and impaired decision-making. Ultimately, the effectiveness of alert generation is judged not only by its speed and accuracy but also by its integration into a comprehensive trading strategy.
4. Market Timing
Market timing, the art and science of anticipating favorable market conditions for trading, is inextricably linked to the functionality of a swing trade scanner. A swing trade scanner's effectiveness hinges on its ability to identify potential entry and exit points within short-term trends. Crucially, the scanner's signals must align with favorable market conditions to maximize potential gains and minimize potential losses. This connection highlights the importance of market timing as a critical component in maximizing the value derived from swing trade scanners. An accurate and relevant market timing strategy can significantly enhance the success rate of trades flagged by the scanner.
The scanner, by itself, does not guarantee market timing accuracy. While identifying potential opportunities through technical analysis, the scanner needs market context. For example, a scanner might flag a stock based on a breakout pattern; however, if the broader market is experiencing a downturn, the scanner's signal loses significance. A robust market timing approach complements the scanner's analysis by considering broader market trends, economic indicators, and overall investor sentiment. This approach can increase the chances of success by filtering out false signals and focusing on opportunities occurring during favorable market conditions. Historical examples demonstrate the importance of considering market contexta stock identified by the scanner might not yield the expected results if the underlying market experiences a downturn during the predicted time frame. The scanner alone cannot predict market behavior; accurate market timing adds a layer of critical, external assessment.
In essence, market timing serves as a crucial filter for the signals generated by a swing trade scanner. Effective market timing enhances the probability of capitalizing on opportunities highlighted by the scanner. By integrating a robust market timing strategy, traders can refine the scanner's output, minimizing false positives and improving the likelihood of making profitable swing trades. However, market timing is not a perfect science. Unforeseen market events, shifts in investor sentiment, and economic volatility can all impact the effectiveness of even the most sophisticated market timing approaches. Therefore, a disciplined approach that combines scanner-generated signals with robust market analysis and risk management practices remains essential for maximizing the benefits of swing trade scanning.
5. Risk Management
Risk management is an indispensable aspect of any trading strategy, particularly when employing a swing trade scanner. The scanner's role is to identify potential opportunities; risk management complements this by mitigating potential losses. A well-structured risk management approach, integrated with the scanner's alerts, significantly enhances the probability of positive outcomes. This exploration examines the vital link between risk management and a swing trade scanner.
- Stop-Loss Orders
Implementing stop-loss orders is fundamental. These predefined orders automatically sell a security when its price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses. A swing trade scanner might identify a trade opportunity, but a subsequent price downturn could lead to substantial losses without a stop-loss. This protective measure ensures that losses are contained, safeguarding capital and preventing larger, potentially devastating, losses. The scanner's signal is only a starting point; a stop-loss order is the proactive protection of capital.
- Position Sizing
Position sizing involves determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade. This ensures that any single trade's potential loss does not jeopardize the entire trading account. A swing trade scanner might flag multiple potential opportunities; appropriate position sizing ensures that each trade's risk is proportionate to the trader's capital. Over-leveraging on a single trade, regardless of a scanner's positive signal, dramatically increases exposure to risk and potentially catastrophic losses. Implementing a methodical position sizing strategy is crucial in the context of a swing trade scanner to maximize potential gains while minimizing the impact of potential losses.
- Risk Tolerance Assessment
Assessing and aligning risk tolerance with potential trades is critical. The scanner provides potential opportunities; the trader's risk tolerance acts as the filter. A trade exceeding the individual's tolerance level, even with a positive scanner signal, could lead to detrimental consequences. A thorough evaluation of individual risk tolerance should guide the implementation of other risk management tools. By understanding and adhering to personal risk tolerance, traders can make more informed decisions about trading based on the scanner's signals. This assessment, alongside a well-constructed strategy, is essential for avoiding emotional trading and potential financial setbacks.
- Diversification
Diversifying investments within a trading strategy is another crucial element. A swing trade scanner might suggest multiple potential opportunities; diversifying across different assets can limit the impact of negative developments in a specific market segment. It involves allocating capital to different instruments and possibly across various sectors, reducing exposure to any single security's risks. This aspect is integral for managing risk within a broader strategy encompassing a swing trade scanner, thereby offering a buffer against potential market downturns. It's essential to maintain a diverse portfolio even when relying on the scanner's signals.
Ultimately, risk management in conjunction with a swing trade scanner is not about eliminating risk entirely. It's about mitigating potential downside. By incorporating stop-loss orders, strategic position sizing, accurate risk tolerance assessment, and diversification, the trader can significantly enhance their probability of success while mitigating potential losses. The value of a swing trade scanner is enhanced when combined with a well-defined risk management plan, effectively transforming a tool for opportunity identification into a potent component of a robust and successful trading approach.
6. Backtesting Capabilities
Backtesting capabilities are essential components of a robust swing trade scanner. The process involves applying a trading strategy, represented by the scanner's algorithms, to historical market data. This allows for a simulated evaluation of the strategy's performance without incurring real financial risk. Accurate backtesting provides crucial insights into the strategy's potential profitability, its consistency, and its susceptibility to market fluctuations. By understanding how a scanner performs under various market conditions, traders can make more informed decisions regarding the scanner's suitability for their trading objectives. Effective backtesting is paramount for validating the scanner's reliability in different market environments.
The practical significance of backtesting lies in its ability to identify potential weaknesses in a trading strategy before deploying it in live trading. A scanner exhibiting inconsistent profitability across various historical periods might suggest inherent flaws in its algorithms or indicators. Real-world examples include a scanner exhibiting consistently high profitability during bull markets but substantial losses during bear markets. This disparity would indicate a need for adjustments to the scanner's criteria or the inclusion of additional factors to improve performance across varying market conditions. Detailed backtesting reports, presenting return rates, win-loss ratios, average trade duration, and maximum drawdown, offer a comprehensive evaluation, allowing traders to make adjustments and refine their strategies. Moreover, the ability to backtest different configurations of the swing trade scanner helps traders find the most optimal settings for maximizing profitability and minimizing risk within their specific investment profiles.
In conclusion, backtesting capabilities are critical for evaluating the long-term viability of a swing trade scanner. It provides valuable insights into potential profitability, consistency, and risk exposure. By simulating real-world market scenarios, traders gain a deeper understanding of the scanner's strengths and weaknesses, allowing them to make informed decisions and adapt their trading strategies accordingly. Ultimately, backtesting serves as a crucial step in ensuring that the scanner aligns with the trader's risk tolerance and financial objectives. However, backtesting, while valuable, does not guarantee future success; real-market conditions can significantly differ from historical data. Furthermore, a scanner's performance on historical data might not accurately predict its future performance. The results of backtesting are valuable, but the trader should conduct further analysis and use their judgment before making actual trades. Diligent examination of backtesting results should factor into a comprehensive trading strategy using a swing trade scanner.
Frequently Asked Questions about Swing Trade Scanners
This section addresses common queries regarding swing trade scanners, providing clarity and context for their use in trading strategies.
Question 1: What is a swing trade scanner, and how does it work?
A swing trade scanner is software designed to identify potential short-term trading opportunities based on predefined criteria. It analyzes historical market data, such as price, volume, and technical indicators. Algorithms within the scanner process this data, flagging instances matching user-defined criteria. These criteria may include patterns like support and resistance levels, candlestick formations, or volume spikes. The scanner then generates alerts informing the user of potential trade setups. However, the scanner is a tool, not a guarantee of success.
Question 2: What are the benefits of using a swing trade scanner?
Scanners can process vast amounts of data significantly faster than humans. This speed enhances the efficiency of opportunity identification. Objectivity reduces emotional bias inherent in human judgment, potentially leading to more rational decision-making. The automation afforded by scanners also frees up valuable trader time for other crucial aspects of their trading strategies.
Question 3: Are swing trade scanners accurate?
Scanner accuracy is variable and depends on the quality and complexity of the algorithms, the historical data employed, and the appropriateness of the criteria. While scanners can identify potential opportunities, they are not infallible. Further due diligence and analysis are essential before acting on any alert generated by the scanner. No automated system guarantees trading success.
Question 4: What are the potential drawbacks of using a swing trade scanner?
False signals, or alerts for trades that do not materialize, are a possibility. Over-reliance on a scanner might lead to a lack of independent market analysis and potentially overlooking important nuances. Scanner alerts must be independently evaluated by the trader and substantiated through further technical or fundamental analysis.
Question 5: How can I choose the right swing trade scanner?
Selecting a suitable scanner depends on individual trading strategies and needs. Key considerations include the scanner's capabilities (data analysis, technical indicator use, alerts), its cost, and the user interface's intuitiveness. Comprehensive research, including thorough reviews and potential backtesting, is critical. Also evaluate how seamlessly the scanner integrates with existing trading platforms or software.
In summary, swing trade scanners can aid in identifying potential swing trade setups, but they are not a substitute for careful trading analysis and independent evaluation. Comprehensive understanding of market conditions, effective risk management, and a well-defined trading strategy remain crucial for success.
Moving forward, let's explore the practical applications of swing trade scanners within specific trading scenarios.
Conclusion
Swing trade scanners represent a powerful tool for identifying potential short-term trading opportunities. Their effectiveness hinges on the accurate analysis of historical market data, including price patterns, volume, and technical indicators. However, the scanner's output requires careful scrutiny and confirmation through supplementary analysis. While automation enhances efficiency and reduces reliance on subjective interpretations, a robust trading strategy encompassing risk management, position sizing, and market context is paramount. Backtesting provides insights into a scanner's potential performance but cannot guarantee future results. Ultimately, the scanner is an aid, not a replacement for independent judgment and thorough due diligence before engaging in any trade.
The evolution of swing trade scanners reflects the ongoing quest for automated market analysis. As technology advances, scanners may become more sophisticated, offering deeper insights and potentially more accurate predictions. However, a balanced approach, integrating scanner signals with independent market analysis and a structured risk management framework, remains crucial for safeguarding capital and achieving long-term trading success. In the dynamic realm of financial markets, continued vigilance and adaptation are essential for maximizing the benefits of these tools and mitigating inherent risks.
Article Recommendations